- Epithelial tissues cover body surfaces, line cavities and form glands.
- They function in protection, secretion, absorption, and transportation.
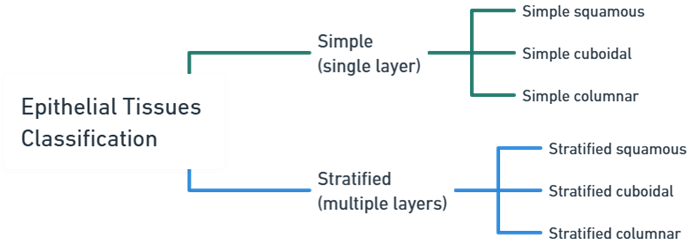
Epithelial tissues are classified based on the number of cell layers and cell shape
Simple Epithelium tissue
- Single layers of cells primarily functions in absorption, secretion, and filtration.
This is a sample ad placement!
Types
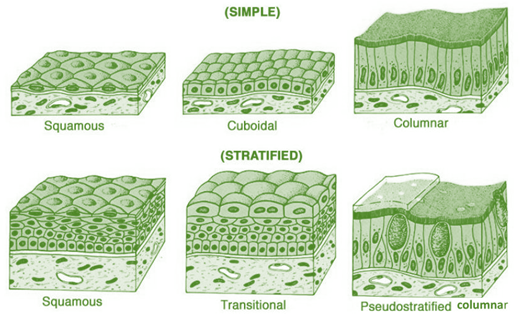
Simple Squamous Epithelium
-
- Structure: Single layer of flat cells.
- Location: Alveoli of lungs, glomeruli of kidneys, lining of blood vessels (endothelium), and lining of body cavities (mesothelium).
- Function: Allows for rapid diffusion and filtration.
This is a sample ad placement!
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
-
- Structure: Single layer of cube-shaped cells.
- Location: Kidney tubules, ducts of small glands, ovary surface.
- Function: Secretion and absorption.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
-
- Structure: Single layer of tall, column-shaped cells.
- Location: Lining of the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, and some ducts of glands.
- Function: Absorption and secretion; may have microvilli for increased surface area or cilia for movement of substances.
This is a sample ad placement!
Stratified Epithelium tissue
- Multiple layers of cells, primarily functions in protection against abrasion.
Types
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
-
- Structure: Multiple layers with flat apical cells.
- Location:
- Keratinized: Epidermis of the skin.
- Non-keratinized: Lining of the mouth, esophagus, and vagina.
- Function: Protects underlying tissues from abrasion and pathogens.
This is a sample ad placement!
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
-
- Structure: Typically, two layers of cube-shaped cells.
- Location: Ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
- Function: Protection and limited secretion/absorption.
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
-
- Structure: Multiple layers with columnar apical cells.
- Location: Rare; found in the male urethra and large ducts of some glands.
- Function: Protection and secretion.
Structure
- Epithelial cells are closely packed together with little extracellular matrix, and they form a continuous sheet held together by cell junctions such as tight junctions, gap junctions, and desmosomes.
- They have an apical surface facing the body cavity or external environment and a basal surface attached to the underlying connective tissue via a basement membrane.
This is a sample ad placement!
Location
- Surface epithelium: External body surfaces (skin), internal cavities (mouth, respiratory tract, and gastrointestinal tract)
- Glandular epithelium: Forms glands (e.g., sweat glands, salivary glands, thyroid gland)
Functions
- Protection: Epithelial tissues protect the body from mechanical injury, harmful substances, and pathogens.
- Secretion: Glandular epithelium secretes substances like hormones, enzymes, and mucus.
- Absorption: Simple columnar and simple cuboidal epithelia help absorb nutrients in the gastrointestinal tract and kidney tubules.
- Transportation: Ciliated epithelial cells help transport particles and mucus across their surfaces.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!
This is a sample ad placement!