Megaloblastic Anemia Introduction
- Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia characterized by the presence of large, abnormal red blood cells (megaloblasts) in the bone marrow and peripheral blood.
- It is primarily caused by deficiencies in vitamin B12 or folic acid, both essential for DNA synthesis.
Causes of Megaloblastic Anemia:
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dietary Deficiency: Insufficient intake of animal products (common in vegans).
- Malabsorption:
- Pernicious Anemia: Autoimmune destruction of stomach cells producing intrinsic factor.
- Surgical Removal: Parts of the stomach or intestines removed surgically.
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Conditions like Crohn’s disease.
- Other Causes:
- Chronic Alcoholism
- Certain Medications: Such as metformin and proton pump inhibitors.
This is a sample ad placement!
Folic Acid Deficiency
- Dietary Deficiency: Poor intake of folate-rich foods (leafy greens, fruits, nuts, beans).
- Increased Demand:
- Pregnancy and Lactation
- Rapid Cell Turnover: Conditions like hemolytic anemia and cancer.
- Malabsorption: Conditions like celiac disease or surgical removal of parts of the intestines.
- Other Causes:
- Chronic Alcoholism
- Certain Medications: Such as methotrexate and anticonvulsants.
Pathophysiology
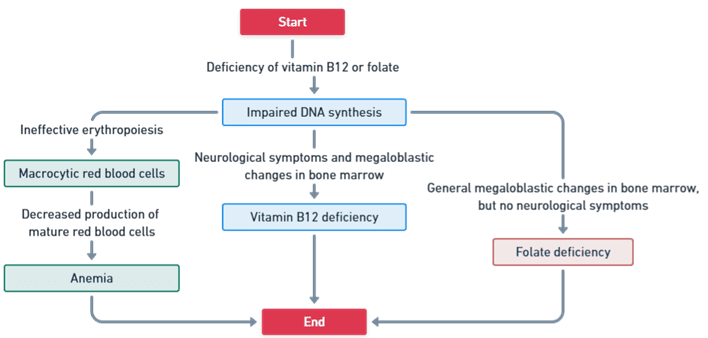
- Disrupted DNA Synthesis: Deficiencies in vitamin B12 or folic acid disrupt DNA synthesis.
- Production of Megaloblasts: Leads to the formation of large, immature red blood cells (megaloblasts).
- Impaired Cell Division: These abnormal cells have an impaired ability to divide and mature properly.
- Ineffective Hematopoiesis: Results in anemia and decreased production of functional blood cells.
This is a sample ad placement!
Symptoms of Megaloblastic Anemia:
- Common symptoms of megaloblastic anemia include:
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Shortness of Breath
- Pale or Jaundiced Skin
- Glossitis: Inflamed, sore tongue.
- Neurological Symptoms (specific to vitamin B12 deficiency):
- Numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
- Balance problems.
- Cognitive disturbances.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
- Diarrhea
This is a sample ad placement!
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis typically involves:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Low hemoglobin, high mean corpuscular volume (MCV).
- Serum Vitamin B12 and Folate Levels: Low levels indicate deficiency.
- Peripheral Blood Smear: Presence of large, oval-shaped RBCs (macrocytes) and hypersegmented neutrophils.
- Bone Marrow Examination: Megaloblastic changes in bone marrow cells.
- Methylmalonic Acid and Homocysteine Levels: Elevated in vitamin B12 deficiency.
Treatment
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dietary Changes: Increase intake of vitamin B12-rich foods (meat, fish, dairy products, fortified cereals).
- Vitamin B12 Supplements:
- Oral Supplements
- Intramuscular Injections: For individuals with absorption issues.
- Treat Underlying Causes: Address gastrointestinal conditions or dietary deficiencies.
This is a sample ad placement!
Folic Acid Deficiency
- Dietary Changes: Increase intake of folate-rich foods (leafy greens, fruits, nuts, beans).
- Folic Acid Supplements: Oral supplementation.
- Treat Underlying Causes: Address malabsorption issues or conditions with increased demand.
Thank you for reading from Firsthope's notes, don't forget to check YouTube videos!

